
Biotechnology is the product of interaction between the biological science and technology. It has been defined as different as the development and utilization of biological forms, products, or processes for obtaining maximum benefits for man and other forms of life. It is in fact, an applied branch of biology.
The term biotechnology was first used by “Karl Ereky” in 1919 to describe a process for the large-scale production of pigs. It uses scientific principles of microbiology, genetics biochemistry, chemistry engineering, mathematics, statistics, computer, industrial processes, etc. The history of biotechnology is as old as human civilization. Development of biotechnology in terms of its growth occurred in two phases traditional and Modern biotechnology.
Major types of Biotechnology

Mainly, there are two types of biotechnology:
Traditional Biotechnology
It was primarily based on fermentation technology using microorganisms in the preparation of curd, ghee, vinegar, yogurt, cheese making, wine, etc. Till that time people did not know how exactly the process occurred and the organisms causing this process. The contributions made by several biochemists and microbiologists over time, could explain the mechanism of the process and also the nature of microorganisms causing the process.
Traditional biotechnology can also include cell cultures products, segments, and sub, or different disease-eradication tactics. But, current biotechnology has a special focus on the industry use of rDNA, cell fusion, and new bioprocessing processes. For the most critical agronomic characteristics, traditional is still the best option. It is due to its easy way and fruitful results with tons of research already done.
Modern Biotechnology
In 1970 a new technique of ‘ recombinant DNA technology was developed and then established by “Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer” in 1973. This technique has changed the overall outlook, then. The technique permits to modification of genetic material for getting new specific products. The combination of biology and production technology based on genetic engineering evolved into modern biotechnology.
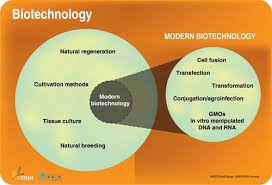
hese breakthroughs paved the way for the evolution of biotechnology from the conventional to the contemporary. In comparison to previous approaches, they are allowed for the regulated and faster production of desired alterations in an organism. These breakthroughs, along with developments in technology and science (such as biochemistry and physiology), opened the door to novel tech applications previously unimaginable.
Principles and Processes
Morden biotechnology is based on two core techniques, genetic engineering, and chemical engineering. Genetic engineering deals with the alternation of genetic material (DNA and RNA). Chemical engineering deals with maintaining the environment for manufacturing a variety of useful products including vaccines, antibiotics, enzymes organic acids, vitamins, etc.
Genetic engineering is defined as the manipulation of genetic material towards the desired end and in a directed and predetermined way, using in vitro process. Manipulation of genes involves repairing defective genes or replacing the effective gene with healthy genes or normal genes; artificially synthesizing new genes; transfer of genes into a new location or a new organism by combining genes from two organisms, altering the genotype; gene cloning, etc. Therefore, genetic engineering is alternatively called recombinant DNA technology or gene cloning.
Overview
Biotechnology has various uses Plant biotechnology, industrial biotechnology, Genomics, microbial biotechnology, environmental and animal biotechnology. But it also has various side effects on the environment and human health.
Effects on the environment are a particular concern about GMO crops and food production. One area of development involves adding pesticides and resistance to specific herbicides. However, herbicide use could be increased, which will have a larger negative effect on the surrounding environment. Also, unintended hybrid strains of weeds and other plants can develop resistance to these herbicides. It happens through cross-pollination, thus negating the potential benefit of the herbicide.
Effects on human health concern on GMO crops could potentially have effects on human health as well. Consumers have developed unexpected allergic reactions. New proteins that have never been ingested before by humans are now part of the foods that people consume every day. Their potential effects on the human body are as of yet unknown.
